With GandCrab stepping out the scene, other malware file encryption filled the gap that concentrates less on customers and more on companies to increase the chances of receiving a bigger payout.
Moving to business objectives.
Malware bytes statistics indicate that consumer systems detections have fallen by 12 percent over the previous year (June 2018–June 2019) and by 25 percent over a quarter. On the other hand, the detection of businesses has risen by 363% since June 2018 and by 14% since the first quarter of 2019.
Ryuk is presently the biggest ransomware risk for companies, according to the stats. Despite its fresh introduction, the malware is ahead of GandCrab, whose operators announced their withdrawal on 1 June.
The US is the primary objective.
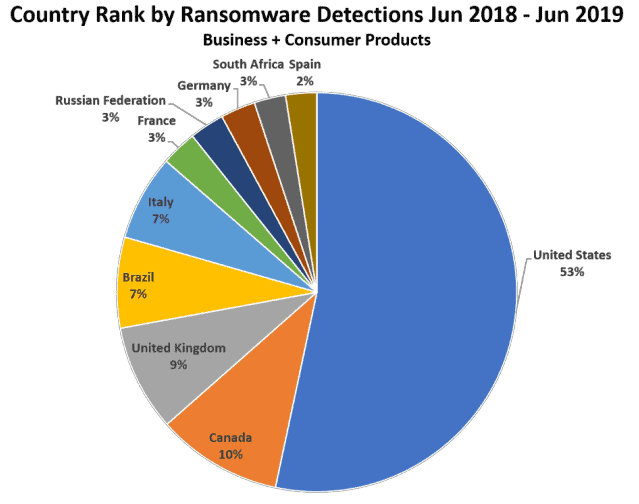
The nation most impacted by ransomware is the USA, according to the worldwide detection statistics of malware by malware of this sort. The company’s telemetry information indicates that 53% of ranches came from this nation, while other areas are far behind. Canada, the second most affected nation on the list, accounts for only 10% of worldwide Malwarebyte ransomware detections, followed by the United Kingdom, with 9%, confirming that the hypothesis that most ransomware target English speaking countries.
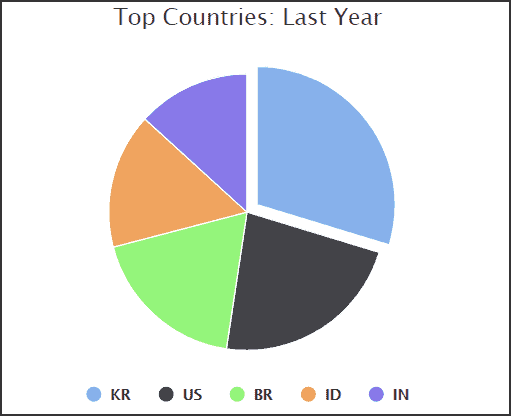
The statistics collected by the ID Ransomware service, which can identify the kind of malware based on the Ransom note or encrypted file, paint a different image. South Korea is the leading nation impacted by file encryption threats, followed by the USA and Brazil.
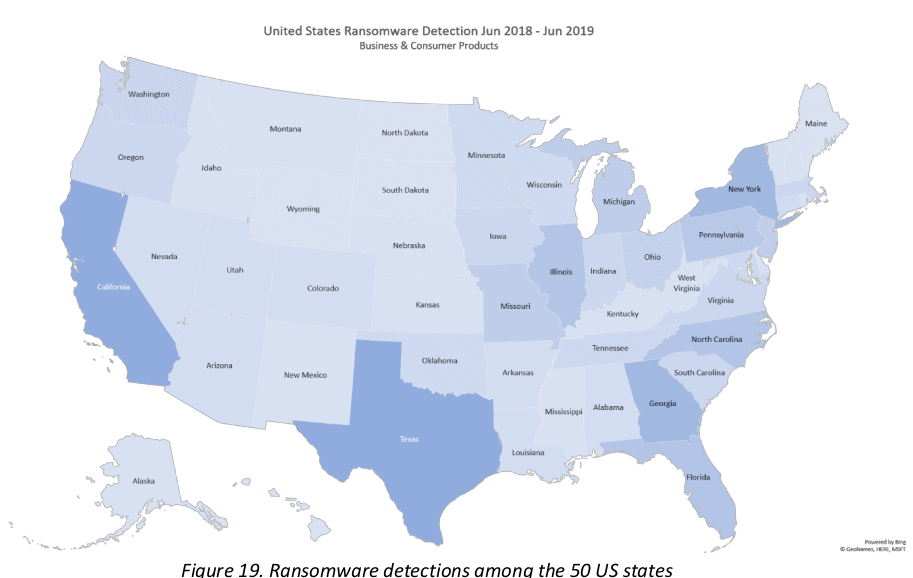
For the previous 12 months, this data includes submissions from around the globe. Further statistical breakdown from malwarebytes indicates that ransomware attacks in Texas and California were most common. Population plays an significant role in distinguishing the goals as customers were the most prevalent victims in populous countries, while company detections originated in industrially blended regions.
Regardless of the target type and the impacted area, ransomware continues at the top of the business threats. As long as firms continue to pay to restore their information, it stays a good company mode for cyber criminals that encourages them to commit fresh assaults. In addition, the economic effect does not stop paying for the ransom because many companies invest in upgrading their safety after a ransomware attack. The establishment of backup processes for live systems and the isolation of copies from the principal network could prevent this.